Personal Zen uses a neuroscience based technique called Attention Bias Modification (ABM) to re-train emotional and attentional patterns that can drive persistent feelings of anxiety and distress. ABM is a family of evidence-based cognitive training interventions that involve screen-based interactions with facial stimuli. Personal Zen is the first clinically validated ABM technique in the form of a mobile game.
Why Faces?
Even before babies can crawl, they can recognize the difference between a smiling face and an angry one. Facial expressions are unique in their ability to capture our attention and drive an emotional response. Through the repetition of interactions that focus attention on a pleasant face, ABM re-trains the associated neural pathways to produce positive mental health outcomes.
Through a decade of placebo-controlled, NIH-funded research and development, Personal Zen is the first and only clinically validated intervention to combine ABM with an engaging mobile game format.
Personal Zen’s proprietary game mechanics have been designed and optimized through a decade of neurocognitive research using:











Personal Zen’s game-based approach to the neurocognitive training technique attention bias modification (ABM) has been widely published in leading peer-reviewed research journals.






Mobile Attention Bias Modification Training Is a Digital Health Solution for Managing Distress in Multiple Sclerosis
Charvet, L., George, A., Cho, H., Crupp, L.B. & Dennis-Tiwary, T. A. (2021)
Purpose: Longitudinal study to investigate Personal Zen’s therapeutic potential in adult and pediatric populations with co-morbid anxiety and chronic illness.
Study Population: Patients (ages 12-24) with pediatric-onset Multiple Sclerosis
Administration: 30 minutes per week over 4 weeks
Primary Endpoints:
Results:
38%
Reduction in adult self-reported anxiety (BAI)
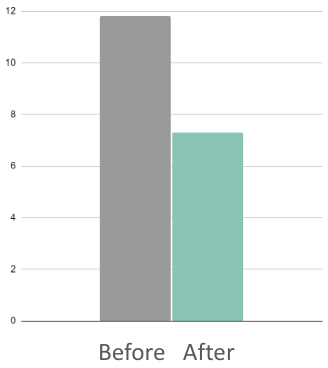
20%
Reduction in youth self-reported anxiety (MASC)
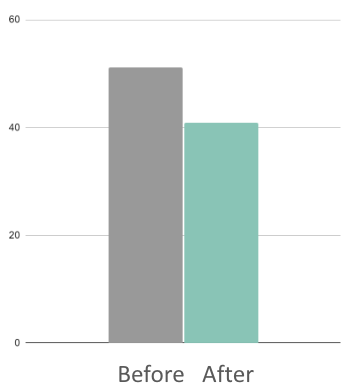
15%
Reduction in negative affect (PANAS)
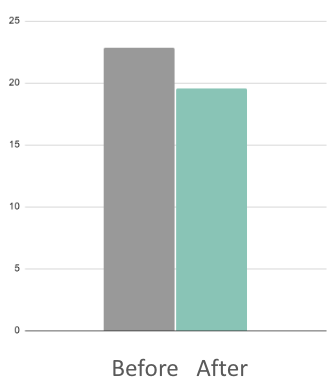

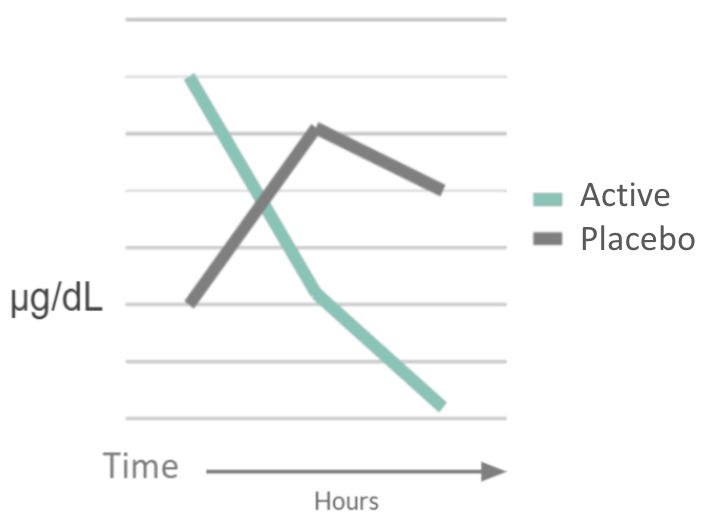
Salutary effects of an attention bias modification mobile application on biobehavioral measures of stress and anxiety during pregnancy
Dennis-Tiwary, T. A., Denefrio, S., and Gelber, S. (2017)
Purpose: Longitudinal study to investigate Personal Zen’s therapeutic potential to treat anxiety and distress during pregnancy.
Study Population: Patients aged 23-45 in their 19th-29th week of pregnancy
Administration: 30 minutes per week for 4 weeks with placebo arm
Primary Endpoints:
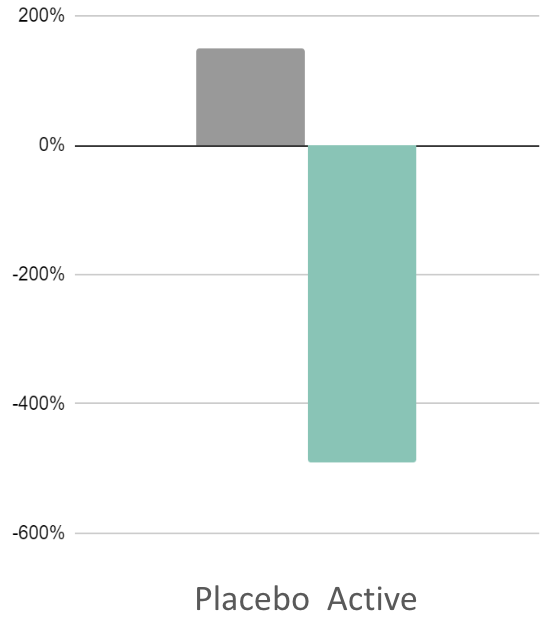
9.4%
Reduction in stress hormone cortisol
(AUC1)
491%
Reduction in cognitive signs of anxiety (DPTM)

For whom the bell tolls: Neurocognitive individual differences in the acute stress-reduction effects of an attention bias modification game for anxiety
Dennis-Tiwary, T. A.,Egan. L. J., Babkirk, S., and Denefrio, S. (2016)
Purpose: To map out individual cognitive differences among patient cohorts with high trait anxiety for game design optimization.
Study Population: Participants aged 18-38 with high trait anxiety, measured via State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI)
Administration: Single session study with placebo arm
Primary Endpoints:
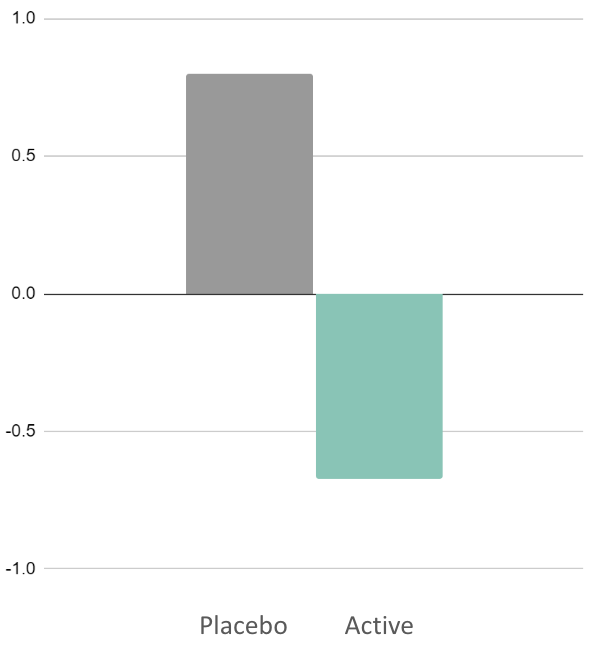
147%
difference in male cognitive control
vs. placebo
(N2)
30%
difference in female stress resilience relative to placebo
(TSST)
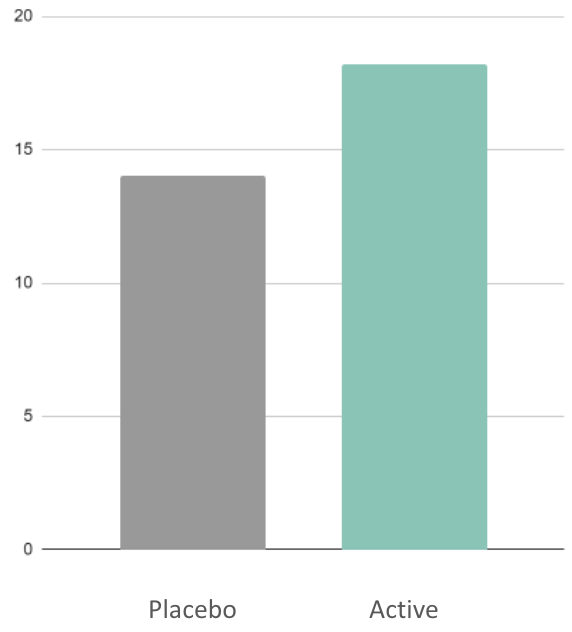

Mental Health on the Go: Effects of a Gamified Attention-Bias Modification Mobile Application in Trait Anxious Adults
Dennis-Tiwary, T. A., and O’Toole, L., J. (2014)
Purpose: Two randomized controlled trials conducted to optimize gameplay dosage and serve as proof of concept studies for individuals with high trait anxiety.
Study Population: Participants aged 18-38 with high trait anxiety, measured via State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI)
Administration: Two separate single-session studies at varying durations with placebo arms
Primary Endpoints:
Short Study
8.9%
Reduction in anxiety
(STAI)
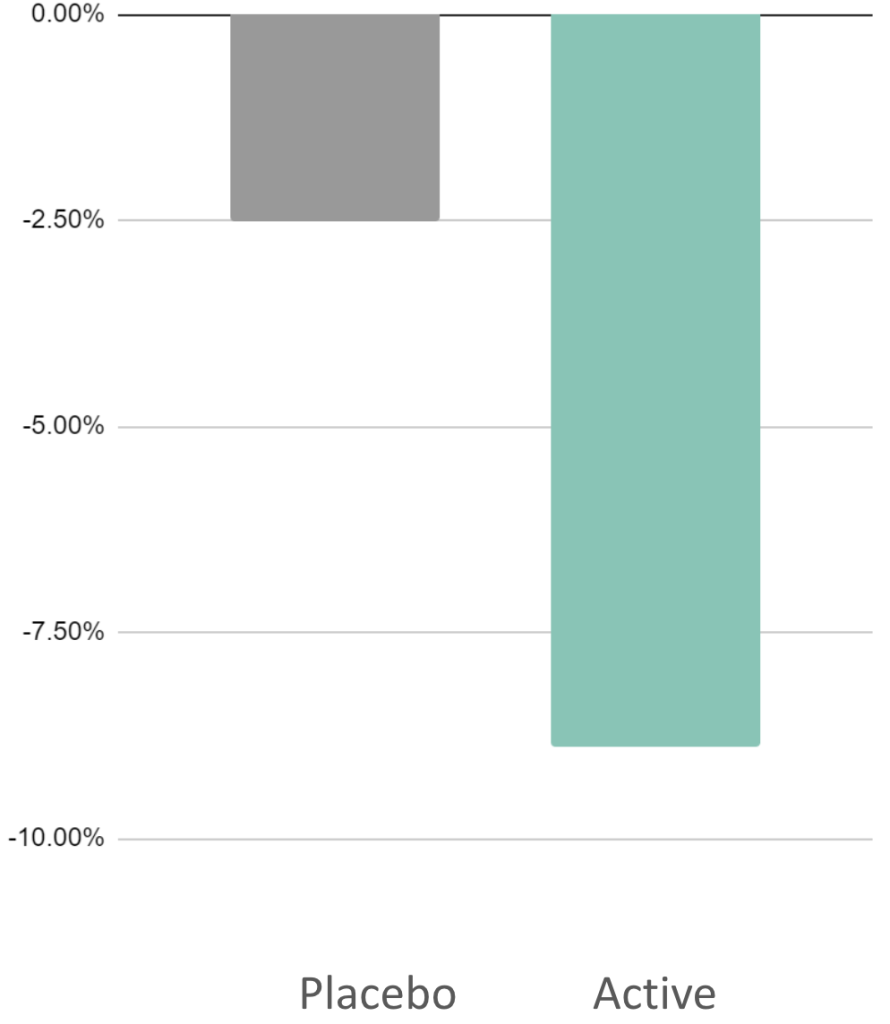
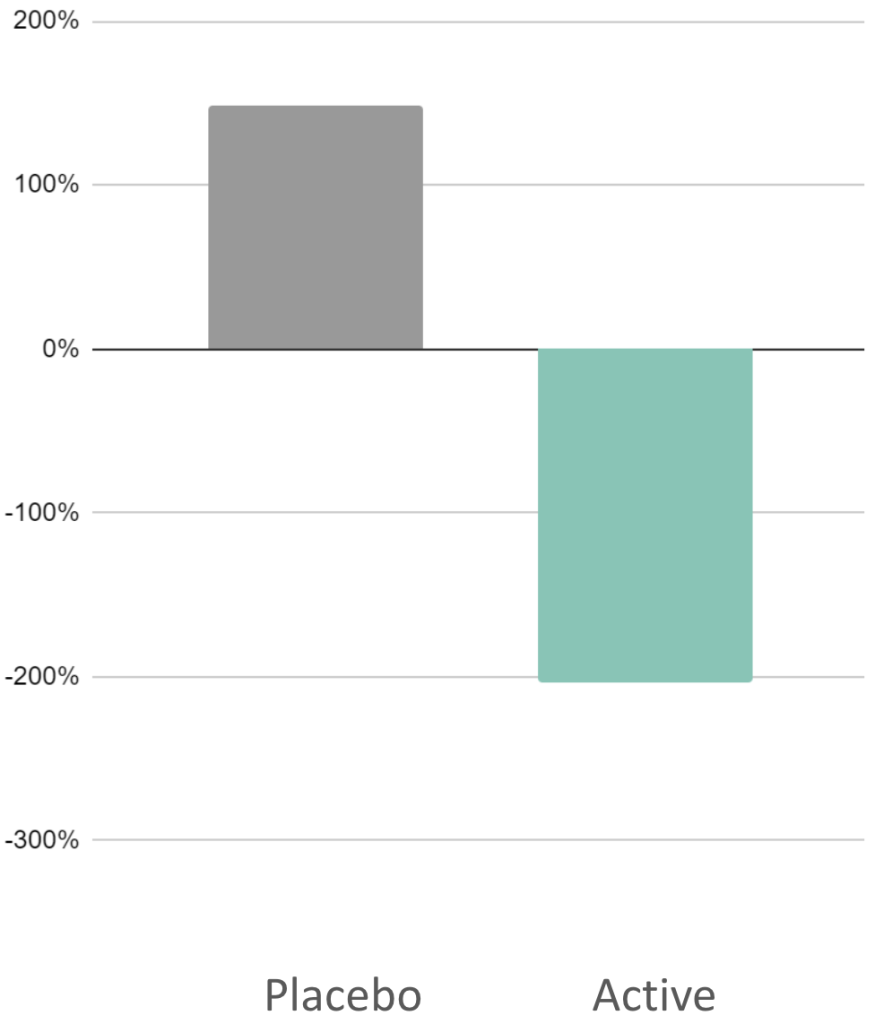
Long Study
204%
Reduction in cognitive signs of anxiety
(DPTM)

tDCS Augments the Effects of Gamified, Mobile Attention Bias Modification
Myruski, S., Cho, H., Bikson, M., & Dennis-Tiwary, T. A. (2021)
Purpose: Study to investigate combination of Personal Zen with neurostimulation to better understand neurobiology of PZ’s mechanism of action.
Study Population: Adults with normal to moderate levels of anxiety measured by DASS-21
Administration: Single session in combination with tDCS neurostimulation headset; placebo tDCS arm
Primary Endpoints:
41.6%
Reduction in self-reported anxiety (AMS)
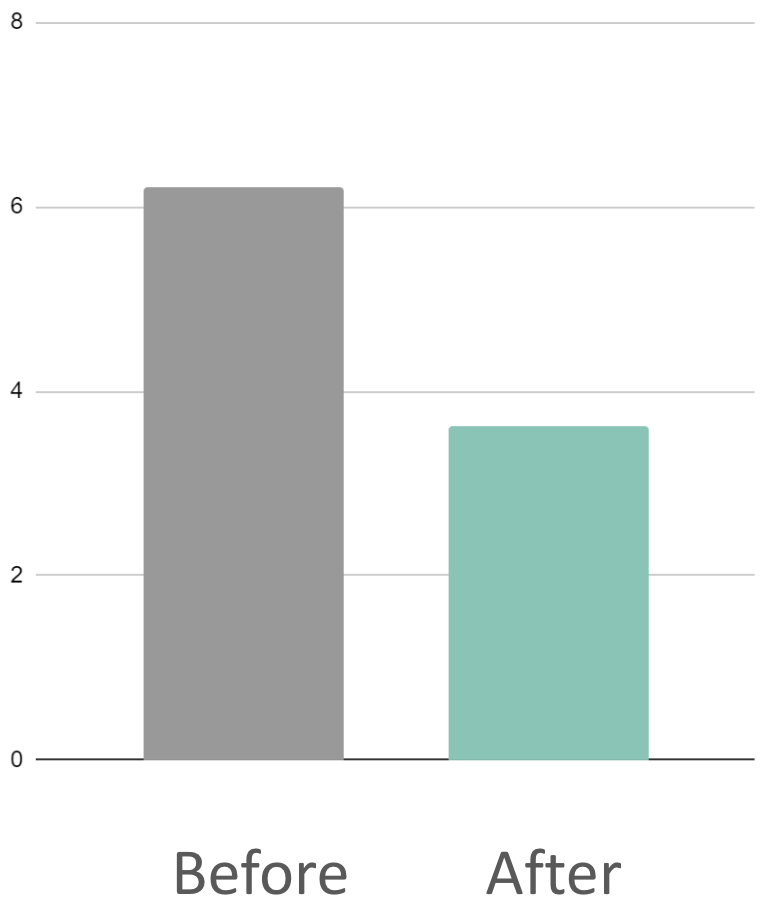
257%
Reduction in cognitive signs of anxiety
(DPTM)
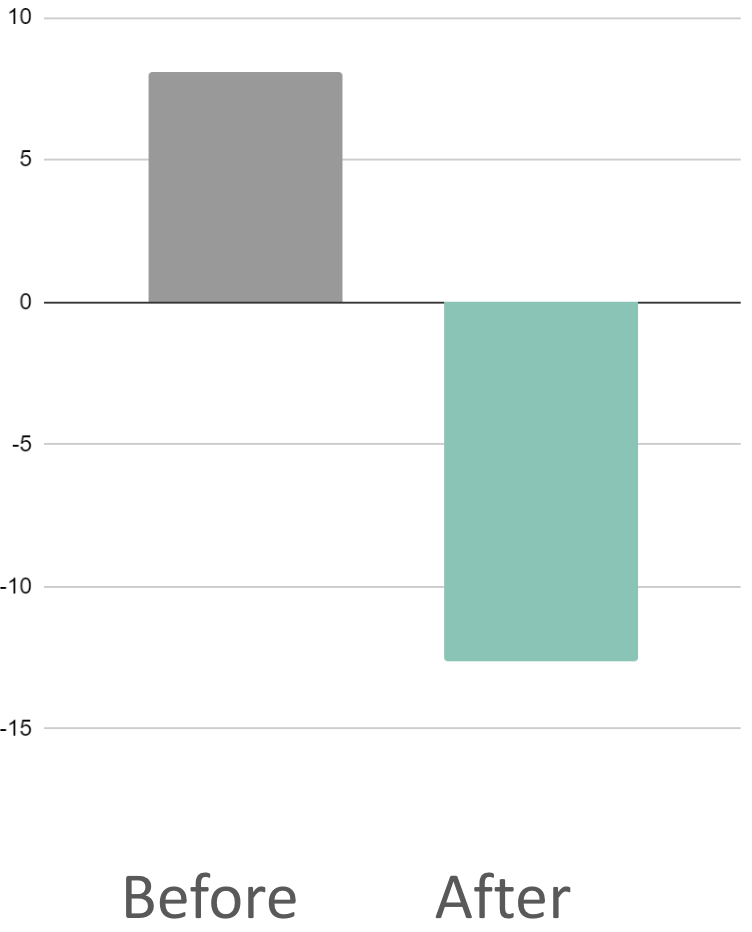
In addition to Personal Zen, Wise is developing its next-generation prescription digital therapeutics (PDTs) to be reviewed and approved by the FDA as prescribed treatments for targeted indications.

Interested in participating in a virtual research study? Email us at virtualtrials@wisedtx.com.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| elementor | never | This cookie is used by the website's WordPress theme. It allows the website owner to implement or change the website's content in real-time. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| _wpfuuid | 11 years | This cookie is used by the WPForms WordPress plugin. The cookie is used to allows the paid version of the plugin to connect entries by the same user and is used for some additional features like the Form Abandonment addon. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| bcookie | 2 years | LinkedIn sets this cookie from LinkedIn share buttons and ad tags to recognize browser ID. |
| lang | session | This cookie is used to store the language preferences of a user to serve up content in that stored language the next time user visit the website. |
| lidc | 1 day | LinkedIn sets the lidc cookie to facilitate data center selection. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _gauges_cookie | past | This cookie is set by Gauges. This cookie helps in improving the webisite by tracking the user behaviour on using the website. |
| _gauges_unique | 1 year | This cookie is set by Gauges. This cookies used for various purposes like proper functioning of the service, marketing and statistical analysis needed for the website. It helps to improve the website by collecting information of the visitors behaviour. |
| _gauges_unique_day | 1 day | These cookie is set by Gauges for various purposes including ensuring proper functioning our Services, marketing and other statistical analyses needed by the website. |
| _gauges_unique_hour | 1 hour | This cookie is set by Gauges. This cookie is used for various purposes like proper functioning of the service, marketing and statistical analysis needed for the website. |
| _gauges_unique_month | 1 month | This cookie are set by Gauges, this is Performance type cookies. They collect information about how visitors use the website and improves the website with this information.This cookie is used for various purposes like proper functioning of the service, marketing and statistical analysis needed for the website. |
| _gauges_unique_year | 1 year | This cookie is set by Gauges. This cookies used for various purposes like proper functioning of the service, marketing and statistical analysis needed for the website. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CONSENT | 2 years | YouTube sets this cookie via embedded youtube-videos and registers anonymous statistical data. |
| _ga | 2 years | The _ga cookie, installed by Google Analytics, calculates visitor, session and campaign data and also keeps track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognize unique visitors. |
| _gat_gtag_UA_159831098_2 | 1 minute | Set by Google to distinguish users. |
| _gat_UA-201403839-1 | 1 minute | A variation of the _gat cookie set by Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager to allow website owners to track visitor behaviour and measure site performance. The pattern element in the name contains the unique identity number of the account or website it relates to. |
| _gcl_au | 3 months | Provided by Google Tag Manager to experiment advertisement efficiency of websites using their services. |
| _gid | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| bscookie | 2 years | This cookie is a browser ID cookie set by Linked share Buttons and ad tags. |
| VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE | 5 months 27 days | A cookie set by YouTube to measure bandwidth that determines whether the user gets the new or old player interface. |
| YSC | session | YSC cookie is set by Youtube and is used to track the views of embedded videos on Youtube pages. |
| yt-remote-connected-devices | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the video preferences of the user using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt-remote-device-id | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the video preferences of the user using embedded YouTube video. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AnalyticsSyncHistory | 1 month | Used to store information about the time a sync with the lms_analytics cookie took place for users in the Designated Countries |
| li_gc | 2 years | Used to store consent of guests regarding the use of cookies for non-essential purposes |
| UserMatchHistory | 1 month | Linkedin - Used to track visitors on multiple websites, in order to present relevant advertisement based on the visitor's preferences. |